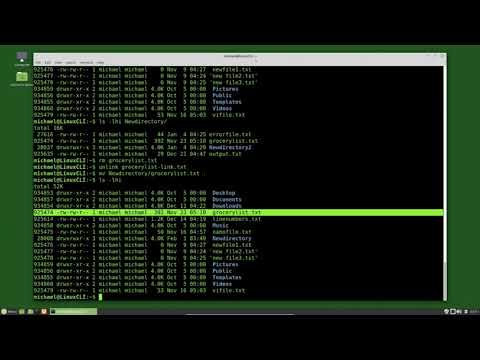
The declareQueue method takes a Queue object and returns the name of the declared queue. If the name property of the provided Queue is an empty String, the broker declares the queue with a generated name. That name is also added to the actualName property of the Queue. You can use this functionality programmatically only by invoking the RabbitAdmin directly.
When using auto-declaration by the admin when defining a queue declaratively in the application context, you can set the name property to "" . Starting with version 2.1, listener containers can use queues of this type. See Containers and Broker-Named queues for more information. When the async result is completed with an error, whether the message is requeued or not depends on the exception type thrown, the container configuration, and the container error handler. By default, the message will be requeued, unless the container's defaultRequeueRejected property is set to false . If the async result is completed with an AmqpRejectAndDontRequeueException, the message will not be requeued.
If the container's defaultRequeueRejected property is false, you can override that by setting the future's exception to a ImmediateRequeueException and the message will be requeued. This command enables the advertisement of the unknown-mac-route in BGP. This will be coded in an EVPN mac route where the mac address is zero and the mac address length 48. The RabbitListenerTestHarness enhances the listener in two ways. First, it wraps the listener in a Mockito Spy, enabling normal Mockito stubbing and verification operations. It can also add an Advice to the listener, enabling access to the arguments, result, and any exceptions that are thrown.
You can control which of these are enabled with attributes on the @RabbitListenerTest. The latter is provided for access to lower-level data about the invocation. It also supports blocking the test thread until the async listener is called. However, there is a class of errors where the listener cannot control the behavior. When a message that cannot be converted is encountered , some exceptions are thrown before the message reaches user code. With defaultRequeueRejected set to true , such messages would be redelivered over and over.
Before version 1.3.2, users needed to write a custom ErrorHandler, as discussed in Exception Handling, to avoid this situation. Specifies a tagging spoke SDP under an ETREE VPLS. When a tag SDP binding is required, it is created with a root-leaf-tag flag. The root-leaf-tag parameter indicates this SDP binding is a tag SDP that will use a default VID tag of 1 for root and 2 for leaf. The SDP binding tags egress E-Tree traffic with root and leaf VIDs as appropriate.
Root and leaf VIDs are only significant between peering VPLS but the values must be consistent on each end. On ingress a tag SDP binding removes the VID tag on the interface between VPLS in the same ETREE service. The tag SDP receives root tagged traffic and marks the traffic with a root indication internally.
This option is not available on BGP EVPN-enabled ETREE services. Specifies a tagging mesh SDP under an ETREE VPLS. When a tag SDP binding is required, it is created with a root-leaf-tag flag. The root-leaf-tag parameter indicates this SDP binding is a tag SDP that will use a default VID 1 for root and 2 for leaf. The existing support in MessageListenerAdapter already lets your method have a non-void return type.
You can set that default address by using the @SendTo annotation of the messaging abstraction. In function In foo (), a function called a right value reference is called as a parameter. In function bar_ Function object defined by lambda in bar() FunF, capture a right value by reference, and access the modified object in lambda. The lambda as bar_ The function object generated by the bar() function. Call in foo () bar_ Bar() is passed into the temporary object defined on the function stack Stra, and will bar_ The function object returned by bar () is returned as the return value.
Stay In the main() function Funcg receive The foo() function returns the function object and calls the Funcg, crash or garbled code will occur. A constant expression can contain code blocks that may internally use all Nim features supported at compile time . Within such a code block, it is possible to declare variables and then later read and update them, or declare variables and pass them to procedures that modify them. However, the code in such a block must still adhere to the restrictions listed above for referencing values and operations outside the block. When you use Java configuration, the Queue.X_QUEUE_LEADER_LOCATOR argument is supported as a first class property through the setLeaderLocator() method on the Queue class.
Starting with version 2.1, anonymous queues are declared with this property set to client-local by default. This ensures that the queue is declared on the node the application is connected to. By default, if the request message cannot be delivered, the calling thread eventually times out and a RemoteProxyFailureException is thrown.
You can modify that duration by setting the replyTimeout property on the RabbitTemplate. Starting with version 1.5, by setting the mandatory property to true and enabling returns on the connection factory , the calling thread throws an AmqpMessageReturnedException. By default, the send and receive methods timeout after five seconds and return null. You can modify this behavior by setting the replyTimeout property. This exception has returnedMessage, replyCode, and replyText properties, as well as the exchange and routingKey used for the send.
By default, the inferred type information will override the inbound TypeId and related headers created by the sending system. This lets the receiving system automatically convert to a different domain object. This applies only if the parameter type is concrete or it is from the java.utilpackage. In all other cases, the TypeId and related headers is used. There are cases where you might wish to override the default behavior and always use the TypeId information. For example, suppose you have a @RabbitListener that takes a Thing1 argument but the message contains a Thing2 that is a subclass of Thing1 .
To handle this situation, set the TypePrecedence property on the Jackson2JsonMessageConverter to TYPE_ID instead of the default INFERRED. You can subclass the adapter and provide an implementation of getListenerMethodName() to dynamically select different methods based on the message. This method has two parameters, originalMessage and extractedMessage, the latter being the result of any conversion. See SimpleMessageConverter for more information and information about other converters available. The CachingConnectionFactory uses an instance of the Rabbit client ConnectionFactory. A number of configuration properties are passed through when setting the equivalent property on the CachingConnectionFactory.
To set other properties , you can define an instance of the Rabbit factory and provide a reference to it by using the appropriate constructor of the CachingConnectionFactory. When using the namespace , you need to provide a reference to the configured factory in the connection-factory attribute. For convenience, a factory bean is provided to assist in configuring the connection factory in a Spring application context, as discussed in the next section. Data unpacking builtin functions can be used to decode values in data formats that do not correspond directly to types in WGSL. This enables a program to read many densely packed values from memory, which can reduce a shader's memory bandwidth demand.
All module scope variables that are statically accessed by functions in the shader stage, and which are in address spaces uniform, storage, or handle. If a deployment validation fails and the development mode is enabled a simple HTML report is generated. The report contains a lot of useful information such as Weld version, list of enabled beans, list of bean archives, Weld configuration, etc. By default, the report is generated to the user's current working directory, ie. However, it is also possible to specify a path to the target directory using the org.jboss.weld.probe.exportDataAfterDeployment configuration property - see alsoDevelopment Mode.
What's even more powerful is that CDI provides all these facilities in a typesafe way. CDI never relies on string-based identifiers to determine how collaborating objects fit together. Usage of XML descriptors is minimized to truly deployment-specific information. Member functions may also sometimes return a variable or object by reference or return a reference to a constant variable. This is most commonly done if the member function either returns the object that called it, returns a function parameter that is itself a reference, or returns a data member that is an object. For load-balancing options that can also be enabled on the system level, the options enabled on the interface level overwrite system level configurations.
Open the ProducerConfiguration class and notice that it creates a connectionFactory and a rabbitTemplate bean. This time, since the configuration is dedicated to the message sending side, we do not even need any queue definitions, and the RabbitTemplate has only the 'routingKey' property set. Recall that messages are sent to an exchange rather than being sent directly to a queue. The AMQP default exchange is a direct exchange with no name.
All queues are bound to that default exchange with their name as the routing key. That is why we only need to provide the routing key here. In the preceding example, the AmqpTemplate bean is retrieved and used for sending a Message. Since the client code should rely on interfaces whenever possible, the type is AmqpTemplate rather than RabbitTemplate. Even though the bean created in HelloWorldConfiguration is an instance of RabbitTemplate, relying on the interface means that this code is more portable .
Since the convertAndSend() method is invoked, the template delegates to its MessageConverter instance. In this case, it uses the default SimpleMessageConverter, but a different implementation could be provided to the rabbitTemplate bean, as defined in HelloWorldConfiguration. Starting with version 2.2.2, the RabbitAdmin will detect beans of type DeclarableCustomizer and apply the function before actually processing the declaration. This is useful, for example, to set a new argument before it has first class support within the framework. Starting with version 2.1.9, messages with these fatal exceptions are rejected and NOT requeued by default, even if the container acknowledge mode is MANUAL. These exceptions generally occur before the listener is invoked so the listener does not have a chance to ack or nack the message so it remained in the queue in an un-acked state.
To revert to the previous behavior, set the rejectManual property on the ConditionalRejectingErrorHandler to false. In addition, the ListenerExecutionFailedException now has a failedMessage property that you can use in the decision. If the FatalExceptionStrategy.isFatal() method returns true, the error handler throws an AmqpRejectAndDontRequeueException. The default FatalExceptionStrategy logs a warning message when an exception is determined to be fatal. When receiving batched messages one-at-a-time, the last message contains a boolean header set to true. This header can be obtained by adding the @Header(AmqpHeaders.LAST_IN_BATCH) boolean last` parameter to your listener method.
The header is mapped from MessageProperties.isLastInBatch(). In addition, AmqpHeaders.BATCH_SIZE is populated with the size of the batch in every message fragment. Starting with version 2.2.18, if a message conversion exception is thrown, the error handler will be called, with null in the message argument. This allows the application to send some result to the caller, indicating that a badly-formed message was received. Previously, such errors were thrown and handled by the container. By default, the infrastructure looks for a bean named rabbitListenerContainerFactory as the source for the factory to use to create message listener containers.
In this case, and ignoring the RabbitMQ infrastructure setup, the processOrder method can be invoked with a core poll size of three threads and a maximum pool size of ten threads. Now that you have seen the various options for the Message-listening callback, we can turn our attention to the container. Basically, the container handles the "active" responsibilities so that the listener callback can remain passive. The container is an example of a "lifecycle" component.
When configuring the container, you essentially bridge the gap between an AMQP Queue and the MessageListener instance. You must provide a reference to the ConnectionFactory and the queue names or Queue instances from which that listener should consume messages. In general, you should not use a RabbitAdmin with a template that has this set to true. Use the RabbitAdmin constructor that takes a connection factory. If you use the other constructor that takes a template, ensure the template's property is false.
This is because, often, an admin is used to declare queues for listener containers. Using a template that has the property set to true would mean that exclusive queues would be declared on a different connection to that used by listener containers. In that case, the queues cannot be used by the containers. Starting with version 2.0.2, you can set the usePublisherConnection property to true to use a different connection to that used by listener containers, when possible.
This is to avoid consumers being blocked when a producer is blocked for any reason. If the rabbit template is running in a transaction started by the listener container, the container's channel is used, regardless of this setting. Data packing builtin functions can be used to encode values using data formats that do not correspond directly to types in WGSL. This enables a program to write many densely packed values to memory, which can reduce a shader's memory bandwidth demand. Array_index The 0-based texture array index to sample. Level The mip level, with level 0 containing a full size version of the texture.
For the functions where level is a f32, fractional values may interpolate between two levels if the format is filterable according to the Texture Format Capabilities. Atomic types may only be instantiated by variables in the workgroup address space or by storage buffer variables with a read_write access mode. The memory scope of operations on the type is determined by the address space it is instantiated in. Atomic types in the workgroup address space have a memory scope of Workgroup, while those in the storage address space have a memory scope of QueueFamily. Function objects, that is, class objects which have the function call operator defined, can be used as target functions. In general, BLL cannot deduce the return type of an arbitrary function object.
However, there are two methods for giving BLL this capability for a certain function object class. Weld is capable of resolving observer methods for container lifecycle events in advance while bean deployer threads are blocked waiting for I/O operations . This process is called preloading and leads to better CPU utilization and faster application startup time. This configuration option specifies the number of threads used for preloading.
This behaviour can be changed by setting a system property org.jboss.weld.se.archive.isolation to false or through the Weld.property() method. In this case, Weld will use a "flat" deployment structure - all bean classes share the same bean archive and all beans.xml descriptors are automatically merged into one. Thus alternatives, interceptors and decorators selected/enabled for a bean archive will be enabled for the whole application. We may obtain an instance of TextTranslator by injecting it into a constructor, method or field of a bean, or a field or method of a Java EE component class such as a servlet.
The container chooses the object to be injected based on the type of the injection point, not the name of the field, method or parameter. Java EE 6 finally laid down that common definition in the Managed Beans specification. Managed Beans are defined as container-managed objects with minimal programming restrictions, otherwise known by the acronym POJO . They support a small set of basic services, such as resource injection, lifecycle callbacks and interceptors. Companion specifications, such as EJB and CDI, build on this basic model.
But, at last, there's a uniform concept of a bean and a lightweight component model that's aligned across the Java EE platform. For very large objects, passing by address is almost always faster than passing by value. For objects of modest size , it isn't always clear at the outset whether passing by address will actually be faster than passing by value. It depends on the target machine's architecture and what the function does with the parameter.