The ideal gas law can be used to calculate the volume of gaseous products or reactants as needed. A gas collected in such a way is not pure, however, but contains a significant amount of water vapor. The measured pressure must therefore be corrected for the vapor pressure of water, which depends strongly on the temperature.
There are several steps involved in this calculation. First, we must determine the question, which is to calculate the volume of a quantity of gas at a given temperature and pressure. In a second step, after establishing a basis, we must convert the mass of methane that will be the basis into pound moles. Third, we must convert temperature in degrees Fahrenheit into absolute degrees Rankin and, fourth, convert pressure from psig into psia. Fifth, we must select the appropriate ideal gas constant and use it with a rewritten form of Equation 4.11 to determine the volume of 11.0 lbs of methane gas.
Finally, we can substitute the values previously determined into the rewritten equation to calculate the volume. Eventually, these individual laws were combined into a single equation—the ideal gas law—that relates gas quantities for gases and is quite accurate for low pressures and moderate temperatures. We will consider the key developments in individual relationships , then put them together in the ideal gas law.
The behavior of gases can be described by several laws based on experimental observations of their properties. The pressure of a given amount of gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature, provided that the volume does not change (Amontons's law). The volume of a given gas sample is directly proportional to its absolute temperature at constant pressure (Charles's law).
The volume of a given amount of gas is inversely proportional to its pressure when temperature is held constant (Boyle's law). Under the same conditions of temperature and pressure, equal volumes of all gases contain the same number of molecules (Avogadro's law). The ideal gas law specifies that the volume occupied by a gas depends upon the amount of substance as well as temperature and pressure. Standard temperature and pressure -- usually abbreviated by the acronym STP -- are 0 degrees Celsius and 1 atmosphere of pressure. Parameters of gases important for many calculations in chemistry and physics are usually calculated at STP. An example would be to calculate the volume that 56 g of nitrogen gas occupies.
Previously, we considered only ideal gases, those that fit the assumptions of the ideal gas law. Gases, however, are never perfectly in the ideal state. When pressure is low and temperature is low, gases behave similarly to gases in the ideal state. When pressure and temperature increase, gases deviate farther from the ideal state. We have to assume new standards, and consider new variables to account for these changes.
A common equation used to better represent a gas that is not near ideal conditions is the van der Waals equation, seen below. The ideal gas law formula states that pressure multiplied by volume is equal to moles times the universal gas constant times temperature. And is a proportionality constant that relates the values of pressure, volume, amount, and temperature of a gas sample.
The variables in this equation do not have the subscripts i and f to indicate an initial condition and a final condition. The ideal gas law relates the four independent properties of a gas under any conditions. Gases whose properties of P, V, and T are accurately described by the ideal gas law are said to exhibit ideal behavior or to approximate the traits of an ideal gas. An ideal gas is a hypothetical construct that may be used along with kinetic molecular theory to effectively explain the gas laws as will be described in a later module of this chapter.
Although all the calculations presented in this module assume ideal behavior, this assumption is only reasonable for gases under conditions of relatively low pressure and high temperature. In the final module of this chapter, a modified gas law will be introduced that accounts for the non-ideal behavior observed for many gases at relatively high pressures and low temperatures. This relationship between temperature and pressure is observed for any sample of gas confined to a constant volume. An example of experimental pressure-temperature data is shown for a sample of air under these conditions in Figure 9.11. In thermodynamics, the volume of a system is an important extensive parameter for describing its thermodynamic state. The specific volume, an intensive property, is the system's volume per unit of mass.
Volume is a function of state and is interdependent with other thermodynamic properties such as pressure and temperature. For example, volume is related to the pressure and temperature of an ideal gas by the ideal gas law. We have just seen that the volume of a specified amount of a gas at constant pressure is proportional to the absolute temperature. In addition, we saw that the volume of a specified amount gas at a constant temperature is also inversely proportional to its pressure. We can correctly assume that pressure of a specified amount of gas at a constant volume is proportional to its absolute temperature. Let us also add the fact that the volume at constant pressure and temperature is also proportional to the amount of gas.
Similarly, the pressure at constant volume and temperature is proportional to the amount of gas. Thus, these laws and relationships can be combined to give Equation 4.10. Is the volume occupied by one mole of a chemical element or a chemical compound. It can be calculated by dividing the molar mass by mass density (ρ). Molar gas volume is one mole of any gas at a specific temperature and pressure has a fixed volume.
If a sample of gas has an initial pressure of 1.56 atm and an initial volume of 7.02 L, what is the final volume if the pressure is changed to 1,775 torr? Assume that the amount and the temperature of the gas remain constant. The volume and temperature are linearly related for 1 mole of methane gas at a constant pressure of 1 atm. If the temperature is in kelvin, volume and temperature are directly proportional. Charles's law states that the volume of a given amount of gas is directly proportional to its temperature on the kelvin scale when the pressure is held constant. This ideal gas law calculator will help you establish the properties of an ideal gas subject to pressure, temperature, or volume changes.
Read on to learn about the characteristics of an ideal gas, how to use the ideal gas law equation, and the definition of the ideal gas constant. To apply this gas law, the amount of gas should remain constant. As with the other gas laws, the temperature must be expressed in kelvins, and the units on the similar quantities should be the same. Because of the dependence on three quantities at the same time, it is difficult to tell in advance what will happen to one property of a gas sample as two other properties change. The best way to know is to work it out mathematically. If a sample of gas has an initial pressure of 375 torr and an initial volume of 7.02 L, what is the final pressure if the volume is changed to 4,577 mL?
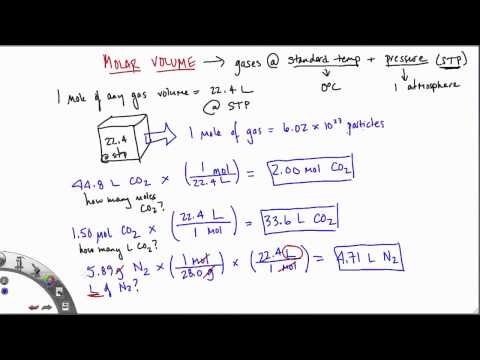
Assume that amount and the temperature of the gas remain constant. The molar volumes of all gases are the same when measured at the same temperature and pressure (22.4 L at STP), but the molar masses of different gases will almost always vary. Examples and practice problems of solving equation stoichiometry questions with gases. We calculate moles with 22.4 L at STP, and use molar mass and mole ratios to figure out how many products or reactants we have.
The ideal gas equation contains five terms, the gas constant R and the variable properties P, V, n, and T. Specifying any four of these terms will permit use of the ideal gas law to calculate the fifth term as demonstrated in the following example exercises. This means equal amounts of moles of gases occupy the same volume under the same conditions of temperature and pressure.
The volume of gas collected and the gas laws can be used to calculate the number of moles of gas collected. We can use the ideal gas equation to calculate the volume of 1 mole of an ideal gas at 0°C and 1 atmosphere pressure. Standard temperature and pressure is defined as 0oC (273.15K) and 1atm pressure.
How To Find The Final Volume Of A Gas The molar volume of a gas is the volume of one mole of a gas at STP. At STP, one mole (6.02×1023 representative particles) of any gas occupies a volume of 22.4L . This relationship shows us that if we increase the moles of gas, n, by adding more gas while maintaining the same temperature and pressure, the volume of gas, V, will also increase. Specific volume is defined as the number of cubic meters occupied by one kilogram of matter. It is the ratio of a material's volume to its mass, which is the same as the reciprocal of its density.
In other words, specific volume is inversely proportional to density. Specific volume may be calculated or measured for any state of matter, but it is most often used in calculations involving gases. If a sample of gas has an initial pressure of 3.66 atm and an initial volume of 11.8 L, what is the final pressure if the volume is reduced to 5.09 L? If a sample of gas has an initial pressure of 1.56 atm and an initial volume of 7.02 L, what is the final volume if the pressure is reduced to 0.987 atm? Temperature is sometimes measured with a gas thermometer by observing the change in the volume of the gas as the temperature changes at constant pressure.
The hydrogen in a particular hydrogen gas thermometer has a volume of 150.0 cm3 when immersed in a mixture of ice and water (0.00 °C). When immersed in boiling liquid ammonia, the volume of the hydrogen, at the same pressure, is 131.7 cm3. Find the temperature of boiling ammonia on the kelvin and Celsius scales. Because the gas is less dense than liquid water, it bubbles to the top of the bottle, displacing the water. Eventually, all the water is forced out and the bottle contains only gas.
B Use the ideal gas law to determine the volume of O2 required under the given conditions. Be sure that all quantities are expressed in the appropriate units. To understand how the ideal gas equation and the stoichiometry of a reaction can be used to calculate the volume of gas produced or consumed in a reaction. Scientists and engineers have defined an ideal gas to be a gas with properties affected only by pressure and temperature. Thus, Equation 4.10 only needs a magical constant so that any one of its variables can be calculated if the other three are known.
That constant is the ideal gas constant R and is used to form the Ideal Gas Law given by Equation 4.11. As we stated earlier, the shape of a gas is determined entirely by the container in which the gas is held. Sometimes, however, the container may have small holes, or leaks. Molecules will flow out of these leaks, in a process called effusion. Because massive molecules travel slower than lighter molecules, the rate of effusion is specific to each particular gas. We use Graham's law to represent the relationship between rates of effusion for two different molecules.
This relationship is equal to the square-root of the inverse of the molecular masses of the two substances. Imagine filling a rigid container attached to a pressure gauge with gas and then sealing the container so that no gas may escape. If the container is cooled, the gas inside likewise gets colder and its pressure is observed to decrease. Since the container is rigid and tightly sealed, both the volume and number of moles of gas remain constant.
If we heat the sphere, the gas inside gets hotter (Figure 9.10) and the pressure increases. 1 mole of an ideal gas occupies a specific volume at a particular temperature and pressure. The most common molar volume is the molar volume of an ideal gas at standard temperature and pressure (273 K and 1.00 atm). If the conditions are not at STP, a molar volume of 22.4 L/mol is not applicable. However, if the conditions are not at STP, the combined gas law can be used to calculate the volume of the gas at STP; then the 22.4 L/mol molar volume can be used. If a gas has an initial pressure of 24,650 Pa and an initial volume of 376 mL, what is the final volume if the pressure of the gas is changed to 775 torr?
Experience has shown that several properties of a gas can be related to each other under certain conditions. The properties are pressure , volume , temperature , and amount of material expressed in moles . What we find is that a sample of gas cannot have any random values for these properties. Instead, only certain values, dictated by some simple mathematical relationships, will occur. If we heat the sphere, the gas inside gets hotter and the pressure increases.
Under these conditions, the volume of the gas will vary inversely with the absolute pressure. This equation calculates a pressure given the corresponding elements of the equivalence; Initial pressure, Initial volume, and temperature. 1 mole of any gas occupies 22.4 dm3 at stp (standard temperature and pressure, taken as 0°C and 1 atmosphere pressure). You may also have used a value of 24.0 dm3 at room temperature and pressure (taken as about 20°C and 1 atmosphere). For a constant volume and amount of air, the pressure and temperature are directly proportional, provided the temperature is in kelvin. Likewise, the only way to decrease the volume of gas, V, while maintaining the same temperature and pressure, is to decrease the moles of gas, n, that are present, that is, remove some of the gas.
Likewise, if we decrease the moles of gas, n, by removing some of the gas while maintaining the same temperature and pressure, the volume of gas, V, will also decrease. Volume is the level at which something is heard or the amount of space a solid, liquid or gas occupies. With sound, its volume is the loudness of the sound. With a container, its volume would be its capacity, or how much it can hold. Volume is often expressed in cubic units determined by the International System of Units.
A gas sample at 35°C has an initial volume of 5.06 L. What is its volume if the temperature is changed to −35°C? Assume that the pressure and the amount of the gas remain constant. A gas sample at 20°C has an initial volume of 20.0 L.
What is its volume if the temperature is changed to 60°C? For the ideal gas equation, note that the product PV is directly proportional to T. Measurement of gas volume contributes to studies on reaction rates and commercial viability of chemical and biochemical processes in which a gas Is a by-product. Additionally measurement of volumes of vapours are also required for determination of molecular weights of volatile liquids by Victor – Meyer method. For example, the space that a substance or 3D shape occupies or contains.
Volume is often quantified numerically using the SI derived unit, the cubic metre. Volumes of some simple shapes, such as regular, straight-edged, and circular shapes can be easily calculated using arithmetic formulas. Volumes of complicated shapes can be calculated with integral calculus if a formula exists for the shape's boundary.
One-dimensional figures and two-dimensional shapes are assigned zero volume in the three-dimensional space. The preceding example was actually a simple problem that has been made more complicated here. The simple solution can provide an estimate for Step 13 of the problem-solving technique in Chapter 1, "Introductory Concepts," in which we judge our results. First, the cracking of ethane into ethylene with the hydrogen being given off doubles the number of moles of gas. Second, the increase of temperature, from 810°R (350°F) to 2,010°R (1,550°F), also more than doubles the volume.




























No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.